Re: Richard J. Lipton • The Art Of Math
Re: Animated Logical Graphs • (30) • (45) • (57) • (58) • (59) • (60) • (61) • (62) • (63) • (64) • (65) • (66) • (69) • (70) • (71) • (72) • (73) • (74)
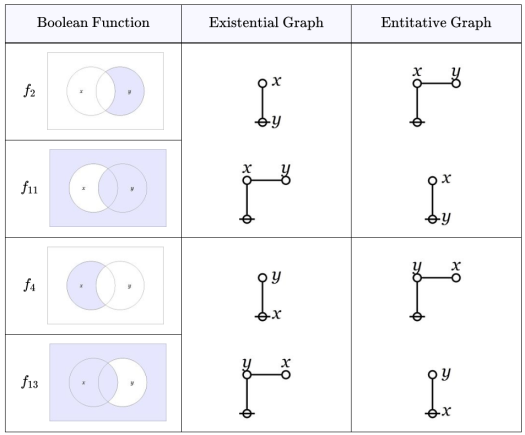
Continuing our scan of the Table in Episode 72, the next two orbits contain the logical graphs for the boolean functions in that order. A first glance shows these two orbits have surprisingly intricate structures and relationships to each other — let’s isolate that section for a closer look.
- The boolean functions
and
are called subtraction functions.
- The boolean functions
and
are called implication functions.
- The logical graphs for
and
are dual to each other.
- The logical graphs for
and
are dual to each other.
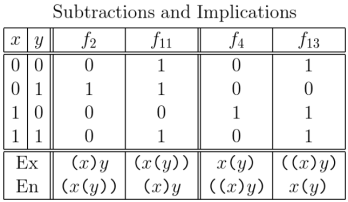
The values of the subtraction and implication functions for each and the text expressions for their logical graphs are given in the following Table.
Resources
- Logic Syllabus • Logical Implication • Truth Tables • Zeroth Order Logic
- Survey of Animated Logical Graphs
cc: Peirce List (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) (13) (14) (15) (16)
cc: Structural Modeling (1) (2) • Systems Science (1) (2)
cc: Cybernetics (1) (2) • Ontolog Forum (1) (2)
cc: FB | Logical Graphs • Laws of Form

Pingback: Survey of Animated Logical Graphs • 4 | Inquiry Into Inquiry
Pingback: Animated Logical Graphs • 76 | Inquiry Into Inquiry
Pingback: Survey of Animated Logical Graphs • 5 | Inquiry Into Inquiry
Pingback: Survey of Animated Logical Graphs • 6 | Inquiry Into Inquiry
Pingback: Survey of Animated Logical Graphs • 7 | Inquiry Into Inquiry
Pingback: Survey of Animated Logical Graphs • 8 | Inquiry Into Inquiry
Pingback: Survey of Animated Logical Graphs • 8 | Systems Community of Inquiry