Mathematical Structure and Logical Interpretation
The main things to take away from the previous post are the following two ideas, one syntactic and one semantic.
- Syntax. The compositional structures of cactus graphs and cactus expressions are constructed from two kinds of connective operations.
- Semantics. There are two ways of mapping the compositional structures of syntax into the compositional structures of propositional sentences.
The two kinds of connective operations are described as follows.
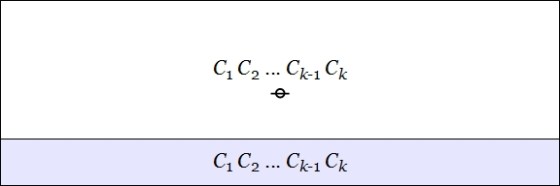
- The node connective joins a number of component cacti
to a node, as shown below.
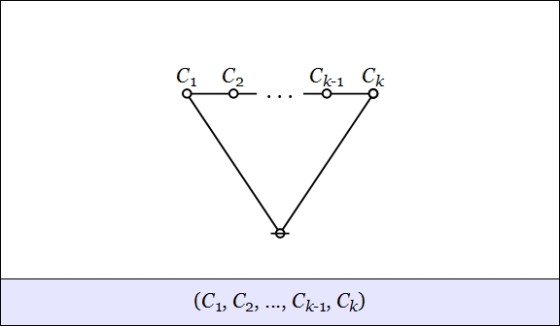
- The lobe connective joins a number of component cacti
to a lobe, as shown below.
The two ways of mapping cactus structures to logical meanings are summarized in Table 3, which compares the entitative and existential interpretations of the basic cactus structures, in effect, the graphical constants and connectives.
Resources
- Theme One Program • Overview
- Theme One Program • Exposition
- Theme One Program • User Guide
- Survey of Theme One Program
cc: FB | Theme One Program • Laws of Form • Mathstodon • Academia.edu
cc: Conceptual Graphs • Cybernetics • Structural Modeling • Systems Science


Pingback: Survey of Theme One Program • 6 | Inquiry Into Inquiry
Pingback: Survey of Theme One Program • 7 | Inquiry Into Inquiry
Pingback: Survey of Theme One Program • 7 | Systems Community of Inquiry