Semiotic Transformations
Re: Transformations of Logical Graphs • (8) • (9) • (10) • (11) • (12) • (13)
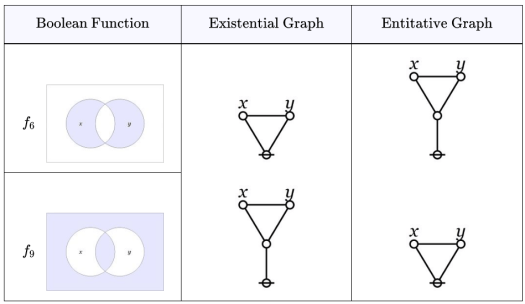
Completing our scan of the Table in Episode 8, the last orbit up for consideration contains the logical graphs for the boolean functions and
The boolean functions and
are known as logical difference and logical equality, respectively. The values taken by
and
for each pair of arguments
in
and the text expressions for their logical graphs are given in the following Table.
Resources
- Logic Syllabus
- Logical Difference • Logical Equality
- Survey of Animated Logical Graphs
- Survey of Semiotics, Semiosis, Sign Relations
cc: FB | Logical Graphs • Laws of Form • Mathstodon • Academia.edu
cc: Conceptual Graphs • Cybernetics • Structural Modeling • Systems Science


Pingback: Survey of Animated Logical Graphs • 7 | Inquiry Into Inquiry
Pingback: Survey of Animated Logical Graphs • 8 | Inquiry Into Inquiry